Title: Understanding Androgenic Alopecia: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
Introduction
Androgenic alopecia, commonly known as male pattern baldness or female pattern hair loss, is a prevalent condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. This form of hair loss can be distressing, but with a comprehensive understanding of its causes, symptoms, and available treatments, you can take proactive steps to manage and potentially reverse its effects. In this article, we will delve into the essential aspects of androgenic alopecia to provide valuable insights and solutions for those experiencing hair loss.
What is Androgenic Alopecia?
Androgenic alopecia is a genetically determined hair loss condition that predominantly affects the scalp. It is caused by a hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a byproduct of the male hormone testosterone. DHT attaches to hair follicles, causing them to shrink and produce thinner and weaker hair strands over time. While it is more commonly associated with men, women can also experience androgenic alopecia, albeit with different patterns and levels of severity.
Causes of Androgenic Alopecia
The primary cause of androgenic alopecia is the sensitivity of hair follicles to DHT. Genetic factors play a crucial role in determining an individual’s predisposition to this condition. If you have a family history of androgenic alopecia, you may be more susceptible to developing it yourself. Other contributing factors include hormonal imbalances, aging, and certain medical conditions.
Symptoms and Progression
The symptoms of androgenic alopecia vary between men and women. In men, it typically starts with a receding hairline, followed by thinning at the crown of the head. As the condition progresses, these areas may merge, leaving only a horseshoe-shaped ring of hair around the back and sides of the scalp. In contrast, women with androgenic alopecia may experience diffuse hair thinning across the scalp, with the hairline remaining intact.
The progression of androgenic alopecia can be gradual or rapid, depending on individual factors. Early detection of symptoms is vital for implementing effective treatment strategies.
Effective Treatments for Androgenic Alopecia
While there is no definitive cure for androgenic alopecia, several treatments have shown promising results in slowing down its progression and stimulating hair growth:
- Minoxidil: A topical over-the-counter medication approved by the FDA for hair loss treatment. Minoxidil promotes hair growth by revitalizing hair follicles and increasing blood flow to the scalp.
- Finasteride: An oral prescription medication that inhibits the conversion of testosterone to DHT, thereby reducing its harmful effects on hair follicles.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): This non-invasive treatment utilizes red light to stimulate hair follicles, leading to improved hair growth.
- Hair Transplantation: In cases of advanced hair loss, hair transplantation surgery can be a viable option. This procedure involves transferring hair follicles from donor areas to the thinning or balding regions of the scalp.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can support overall hair health.
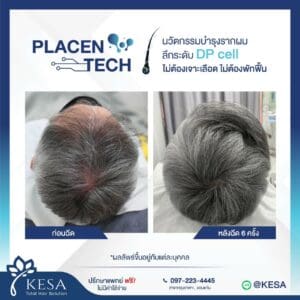
Conclusion
Androgenic alopecia is a widespread condition that can affect both men and women, causing distress and affecting self-esteem. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial in managing hair loss effectively. If you or someone you know is experiencing hair loss symptoms consistent with androgenic alopecia, seeking professional advice from a dermatologist or hair specialist is recommended. Early intervention and the right approach can significantly impact hair health and lead to improved confidence and well-being.
