Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss in both men and women. This condition can be emotionally distressing, and understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the details of alopecia areata, offering valuable insights to help you better manage this condition.
What Is Alopecia Areata ?
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that targets hair follicles, leading to hair loss. The immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, causing hair to fall out in small, round patches on the scalp, face, or other parts of the body. This condition can affect anyone at any age and often occurs suddenly.
Causes of Alopecia Areata
The exact cause of alopecia areata is still under research, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Genetics: A family history of autoimmune diseases can increase the risk of developing alopecia areata.
- Autoimmune Response: The immune system’s response to healthy hair follicles can trigger hair loss.
- Co-morbid disease : Thyroid disease, Vitiligo, Androgenic alopecia, Atopic dermatitis.
- Environmental Factors: Stress, viral infections, and other environmental factors may play a role in triggering alopecia areata in susceptible individuals.
Symptoms of Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata typically presents with the following symptoms:
- Hair Loss: The most prominent symptom is hair loss in small, round patches.
- In severe case, Hair loss extend entire scalp called “Alopecia totalis”
- Regrowth: Hair may regrow in affected areas, but it can also fall out again.
- Nail Changes: Some individuals may experience nail abnormalities, such as pitting or ridges.

Diagnosis of Alopecia Areata
- Diagnosing alopecia areata usually involves a physical examination, Trichiscope and, in some cases, a scalp biopsy.
- Dermatologists may also evaluate family medical history to confirm the diagnosis.
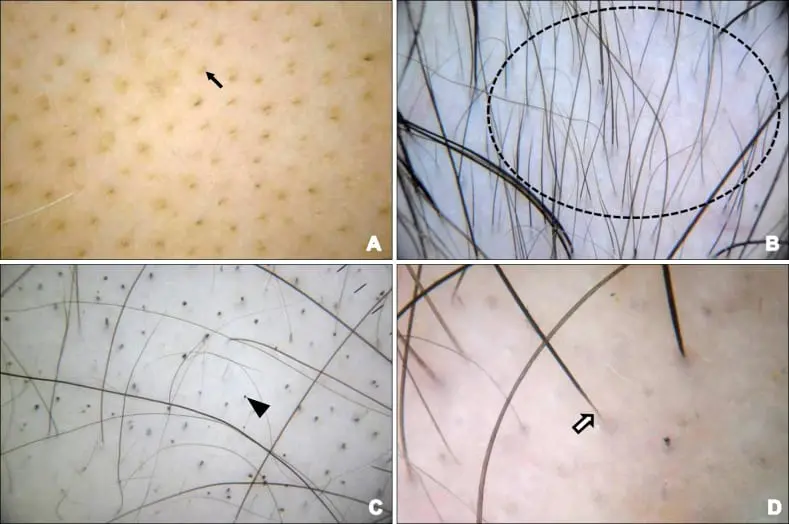
Trichoscope finding in Alopecia areata patient
Reference : www.researchgate.net
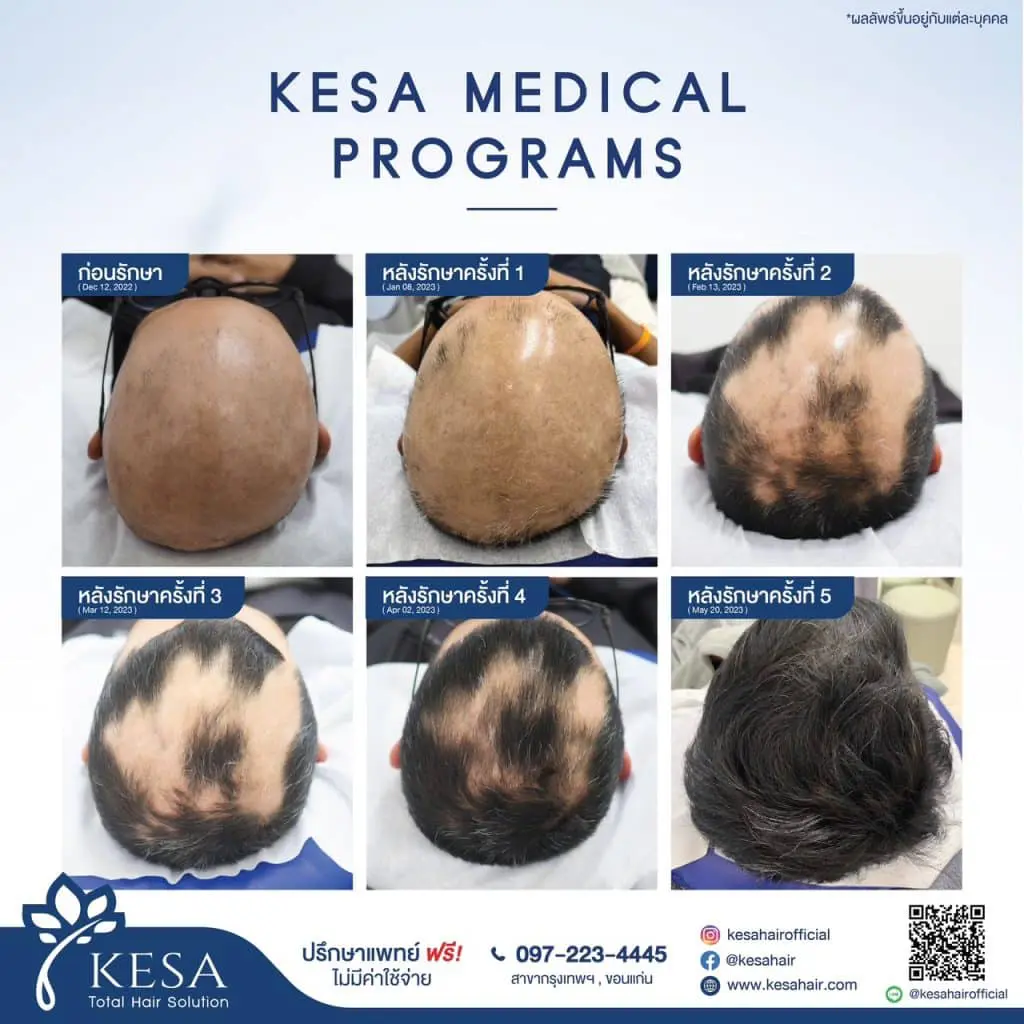
Treatment of Alopecia Areata
Managing alopecia areata varies depending on the individual’s specific case. Some common treatment options include:
- Topical Corticosteroids: These creams or ointments can help reduce inflammation and promote hair regrowth.
- Intralesional Corticosteroid Injections: Dermatologists may inject corticosteroids directly into the affected areas to stimulate hair growth.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment involves applying chemicals to the scalp to provoke an allergic reaction, which can stimulate hair regrowth.
- Minoxidil can help stimulate new hair growth.
- Hair Restoration: In some cases, hair restoration techniques like hair transplants or wigs may be considered.
Coping Strategies
Living with alopecia areata can be challenging. Coping strategies include:
- Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and helpful tips for managing the condition.
- Hairstyling: Experiment with hairstyles that help conceal hair loss and boost confidence.
- Counseling: Seek professional counseling or therapy to address the emotional impact of alopecia areata.
Conclusion
Alopecia areata is a complex condition with no known cure, but various treatment options can help manage its symptoms. If you or someone you know is affected by alopecia areata, consult with a dermatologist for a personalized treatment plan. Remember that emotional support and coping strategies are essential components of managing this condition. Stay informed, stay positive, and don’t hesitate to seek help when needed.
